Reinforced concrete is a widely used building material known for its high strength and durability. Its versatility and adaptability make it suitable for various construction projects, ranging from residential buildings to massive infrastructure developments. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of designing reinforced concrete structures, exploring key considerations, design principles, and best practices. Join us as we explore the fascinating world of design reinforced concrete.
I. Understanding Reinforced Concrete:
To design reinforced concrete structures effectively, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of its composition and properties. Reinforced concrete consists of two main components: concrete and reinforcement. Concrete is a composite material made up of cement, water, fine and coarse aggregates, while reinforcement typically takes the form of steel bars or mesh. The combination of these materials creates a synergy that enhances the overall strength and load-bearing capacity of the structure.
II. Structural Design Principles:
Designing reinforced concrete structures requires careful consideration of various principles to ensure safety and functionality. These principles include determining design loads, analyzing structural stability, and detailing reinforcement. Design loads encompass both dead loads (permanent loads such as the weight of the structure itself) and live loads (temporary loads from occupants, furniture, or environmental factors). By accurately assessing these loads, engineers can determine the appropriate dimensions and reinforcement requirements for the structure.
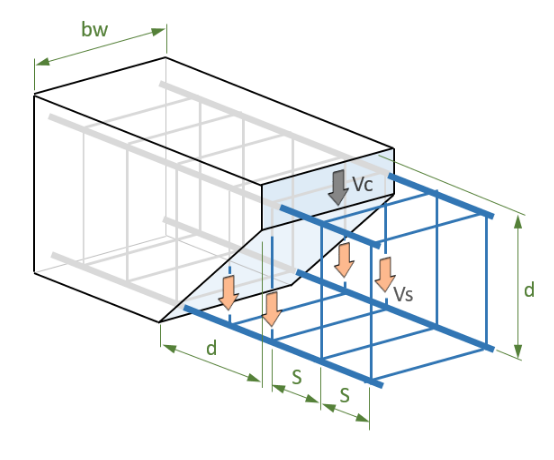
Analyzing structural stability involves assessing the forces acting on the structure, such as gravity, wind, seismic activity, or temperature changes. This analysis allows engineers to determine the required reinforcement and design appropriate structural elements, such as beams, columns, and slabs. Detailing reinforcement involves specifying the exact placement, size, and configuration of reinforcement bars to ensure optimal structural integrity and prevent potential weaknesses or failure points.
III. Design Methods and Codes:
In designing reinforced concrete structures, adherence to recognized design methods and codes is essential to ensure compliance with safety standards. Various design methods exist, including the Working Stress Design (WSD) and the Load and Resistance Factor Design (LRFD). The WSD method focuses on limiting stresses within acceptable ranges, while the LRFD method considers both strength and load factors to ensure a higher level of safety.
Design codes, such as the American Concrete Institute (ACI) Code, Eurocode, or Indian Standard Code, provide specific guidelines and requirements for reinforced concrete design. These codes cover a wide range of aspects, including material selection, design approaches, detailing requirements, and construction considerations. Adhering to these codes helps ensure that structures are designed and built to withstand anticipated loads and environmental conditions.
IV. Advanced Design Considerations:
As the field of engineering advances, new design considerations and techniques continue to emerge, enhancing the performance and sustainability of reinforced concrete structures. Some of these considerations include:
a. Durability: Designing for durability involves selecting appropriate materials, such as high-performance concrete and corrosion-resistant reinforcement, to minimize deterioration caused by chemical attacks, weathering, or aggressive environments.
b. Sustainability: With growing environmental concerns, designing sustainable reinforced concrete structures has become increasingly important. This involves optimizing material usage, incorporating recycled materials, and considering energy-efficient construction techniques.
c. Structural Health Monitoring: Implementing structural health monitoring systems allows engineers to assess the condition of a structure throughout its lifespan. This technology helps identify potential defects or deterioration, enabling early intervention and maintenance.
Conclusion:
Designing reinforced concrete structures requires a meticulous approach, considering various principles, design methods, and codes. By understanding the composition and properties of reinforced concrete, engineers can create robust and safe structures. As the field evolves, advanced considerations like durability, sustainability, and structural health monitoring play significant roles in ensuring the longevity and performance of these structures.
We hope this blog post has provided you with valuable insights into the world of design reinforced concrete. If you have any questions, suggestions, or personal experiences in designing reinforced concrete structures, we invite you to share them in the comments section below. Let’s continue the conversation!
Design of Reinforced Concrete: McCormac, Jack C., Brown, Russell …
Design of Reinforced Concrete, 10th Edition by Jack McCormac and Russell Brown, introduces the fundamentals of reinforced concrete design in a clear and … – www.amazon.com

Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Special Moment Frames: A …
This Guide is written to describe the use, analysis, design, and construction of special reinforced concrete moment frames. NIST GCR. 11-917-11REV-1, Seismic … – nvlpubs.nist.gov
EM 1110-2-2104, Strenght Design for Reinforced Concrete ydraulic …
Nov 30, 2016 … This manual covers requirements for design of reinforced concrete hydraulic structures by the strength design method. It is applicable to all … – www.publications.usace.army.mil
Reinforced Concrete Design
A problem unique to the design of reinforced concrete structures is the need to detail each member throughout. Steel structures, in general, require only the … – www.ce.memphis.edu
Reinforced concrete structural design optimization: A critical review …
Jul 1, 2020 … As the construction of reinforced concrete (RC) structures consumed tremendous amounts of steel reinforcement and concrete, RC structural design … – www.sciencedirect.com

Design Reinforced Concrete
Reinforced Concrete Design Software | SkyCiv Integrated seamlessly with Structural 3D the Reinforced Concrete Design module supports concrete beam and column design for a variety of building codes.Run and optimize the concrete section designs calculations on your entire 3D structure in just a few cl – drawspaces.com
LIMIT STATE DESIGN OF REINFORCED CONCRETE – P. C. …
… The two books together cover all the topics in IS 456 : 2000 and many other topics which are so important in modern methods of design of reinforced concrete. – books.google.com
Reinforced Concrete Design | SkyCiv Engineering
Sep 2, 2022 … Reinforced Concrete is the common term given to a concrete member (or slab) that contains steel reinforcement (usually in the form of steel bars) … – skyciv.com
Reinforced Concrete Hatch Autocad
Reinforced Concrete Hatch Autocad Reinforced Concrete Hatch Autocad – Autocad Space Apr 7 2021 … Simply move the snapbase run hatchedit select the hatch and hit okay without doing anything. This will regenerate the hatch to the new … /a /p /p !– /wp:paragraph — /div !– /wp:column — !– wp:co – drawspaces.com